-
Internal Combustion Piston Engines
| Nr. | Chapter | Page. |
| Two-stroke engine | ||
| History | ||
| How it works | ||
| Design types | ||
| Four-stroke engine | ||
| History | ||
| How it works | ||
| Strokes | ||
| Two-stroke vs four-stroke | ||
| Advantages | ||
| Disadvantages | ||
| Possible improvements for disadvantages | ||
| References |
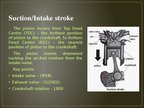
Exhaust stroke
Again the momentum of flywheel moves the piston up from BDC to TDC thereby driving the exhaust gases outside through the exhaust valve.
Key points:
Intake valve – CLOSED
Exhaust valve – OPEN
Crankshaft rotation – 180°(total = 720°)
Two-stroke vs Four-stroke
Two-stroke
Lighter;
More efficient;
Ability to use lower-grade fuel;
More cost-efficient;
Higher power-to-weight ratio (more power for less weight);
Ideal for ships, motorcycles and lawn mowers.
Four-stroke
More possible maneuverability;
Require less lubrication;
Larger thermal efficiency;
Ideal for automobiles like cars and trucks.
Advantages
Size of engine is very less compared to external combustion engines;
Power-to-weight ratio is high;
Very suitable for small power requirement applications;
Usually more portable than their counterpart external combustion engines;
Safer to operate;
Starting time is very short;
High efficiency than external combustion engine;
No chances of leakage of working fluids;
Requires less maintenance;
Lubricant consumption is less as compared to external combustion engines.
…
Internal combustion piston engines Two-stroke and four-stroke engines - history, how it works, design types Two-stroke vs four-stroke Advantages Disadvantages Possible improvements for disadvantages